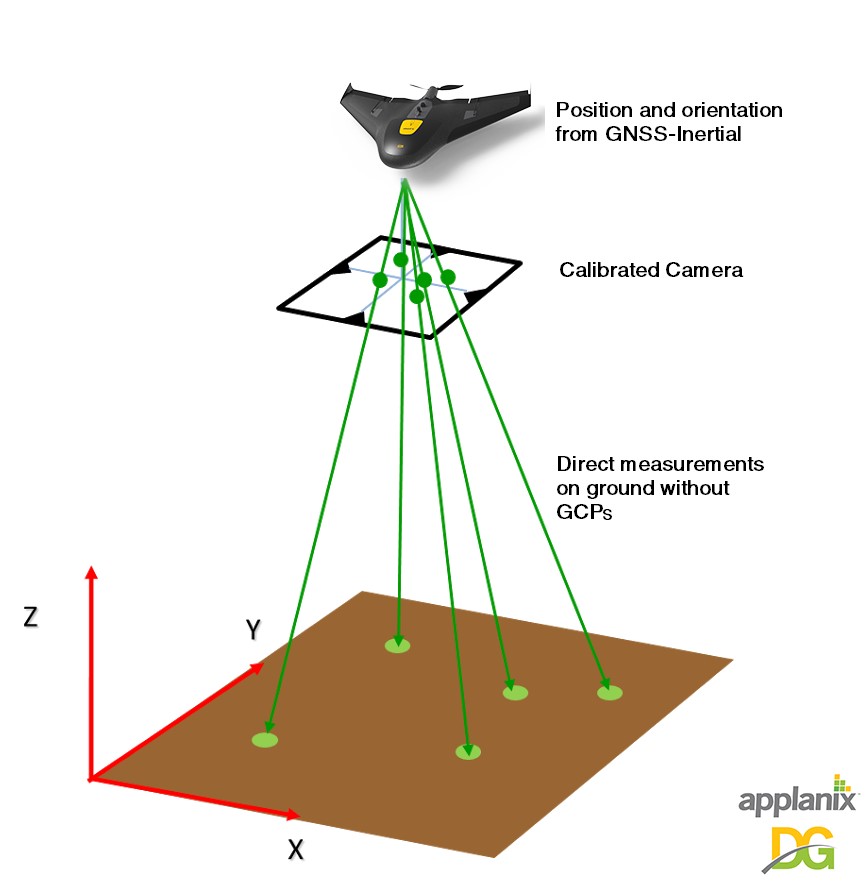
DG is a term Applanix first started to use to describe how our GNSS-Inertial technology is used to reduce the cost and improve the efficiency of aerial survey. Some in the industry have adopted the term as a catch-all for Aerial Triangulation, but it’s important not to confuse these two terms, as there is a huge difference in efficiency and accuracy.
DG refers to computing the position and orientation of an imaging payload to a very high degree of accuracy and precision using multi-frequency, multi-constellation RTK and post-processed carrier phase Differential GNSS tightly integrated with calibrated inertial sensors for the purpose of high accuracy mapping. For Photogrammetric applications, the Exterior Orientation (EO) of each image is pre-computed before any point-matching or adjustment phase. Unlike a PPK position only DGNSS solution, having the full position and orientation eliminates all issues associated with automatic project set-up, failed point matching and reduced sidelap.
Applanix DG solutions work with all airborne mapping sensors, including LiDAR, RGB cameras, NIR cameras, Thermal cameras, SAR, Multispectral and Hyperspectral cameras. The georeferencing can be done in real-time, or for highest accuracy in post-mission using Applanix POSPac UAV Software.
DG for UAVs
Applanix has decades of experience in multi-frequency, multi-constellation Differential GNSS and inertial based positioning and orientation. We have engineered this technology for use with the very best in small-form factor hardware and powerful software, to produce a DG solution for professional aerial mapping on UAVs:
- built for the unmanned aerial environment
- rugged yet lightweight
- powerful but not power-hungry
- custom designed components engineered to tightly integrate all of the enabling technologies
- proven accuracy
- global support
Read More
There is a very interesting article in Commercial UAV News about Applanix DG with LIDAR on a UAV. Pierre Chaponnière from YellowScan talked up the benefits of Direct Georeferencing (and Applanix APX-15 UAV) for LiDAR / Photogrammetry vs Traditional Aerial Triangulation systems.